Security in Machine Learning
Data/Information security and privacy are increasingly important as ML methods become more powerful. Federated Learning (FL) serves as a method for
- protecting data security and privacy by keeping data localized
- parallelizing large-scale models through a divide-and-conquer approach
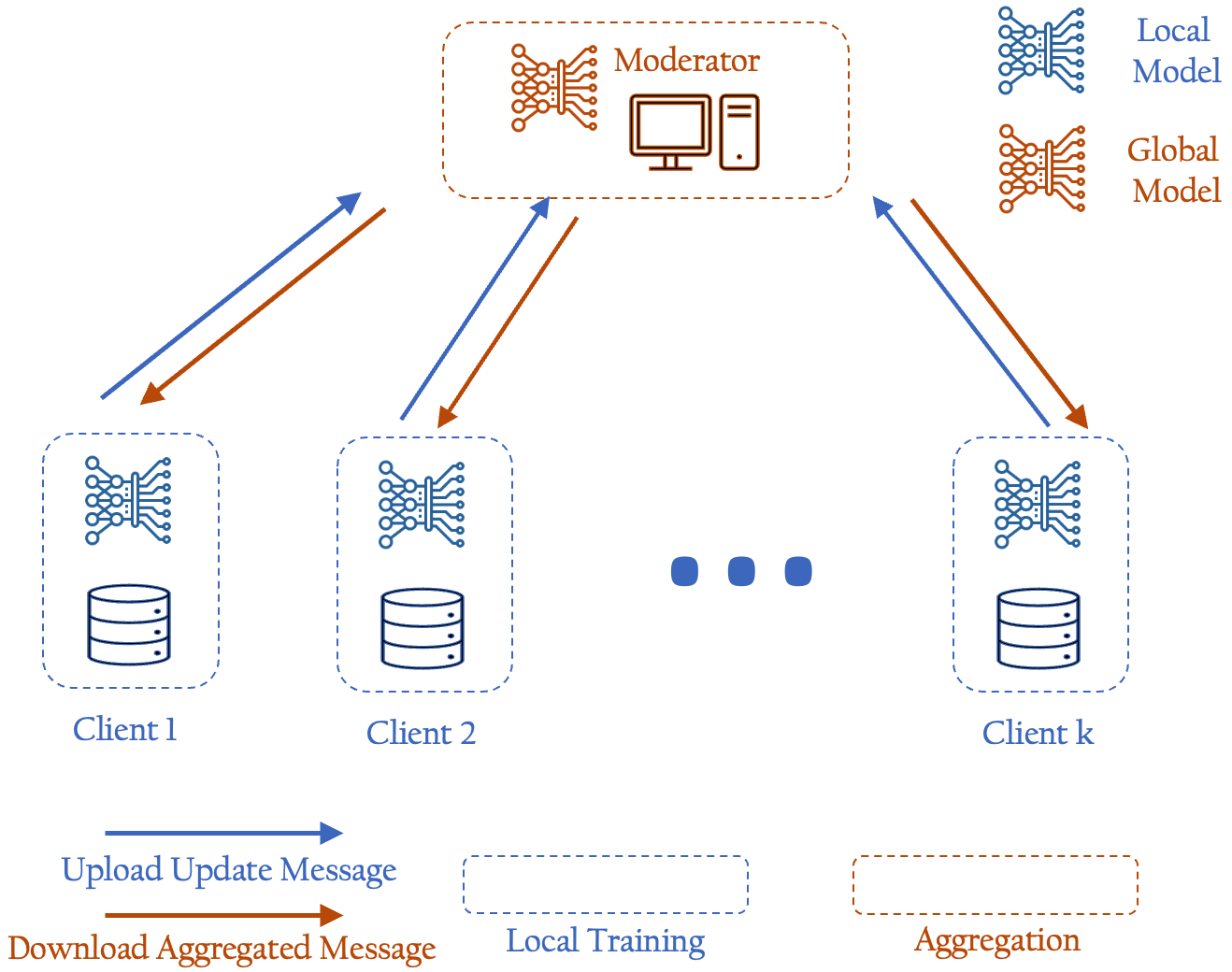
For FL algorithm efficiency, the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM) is a commonly used distributed/consensus optimization method for collaborative model training. Despite the data availability, FL also faces the following issues:
- Data distribution across clients: if data is distributed non-identically across nodes, it could negatively impact model convergence
- Privacy in model transmission: membership inference attacks, model inversion attacks
- Robustness in training: data poisoning attacks, Byzantine attacks, backdoor attacks
We work on FL schemes specifically to address these malicious attacks and to enhance efficiency and robustness of the training process.
